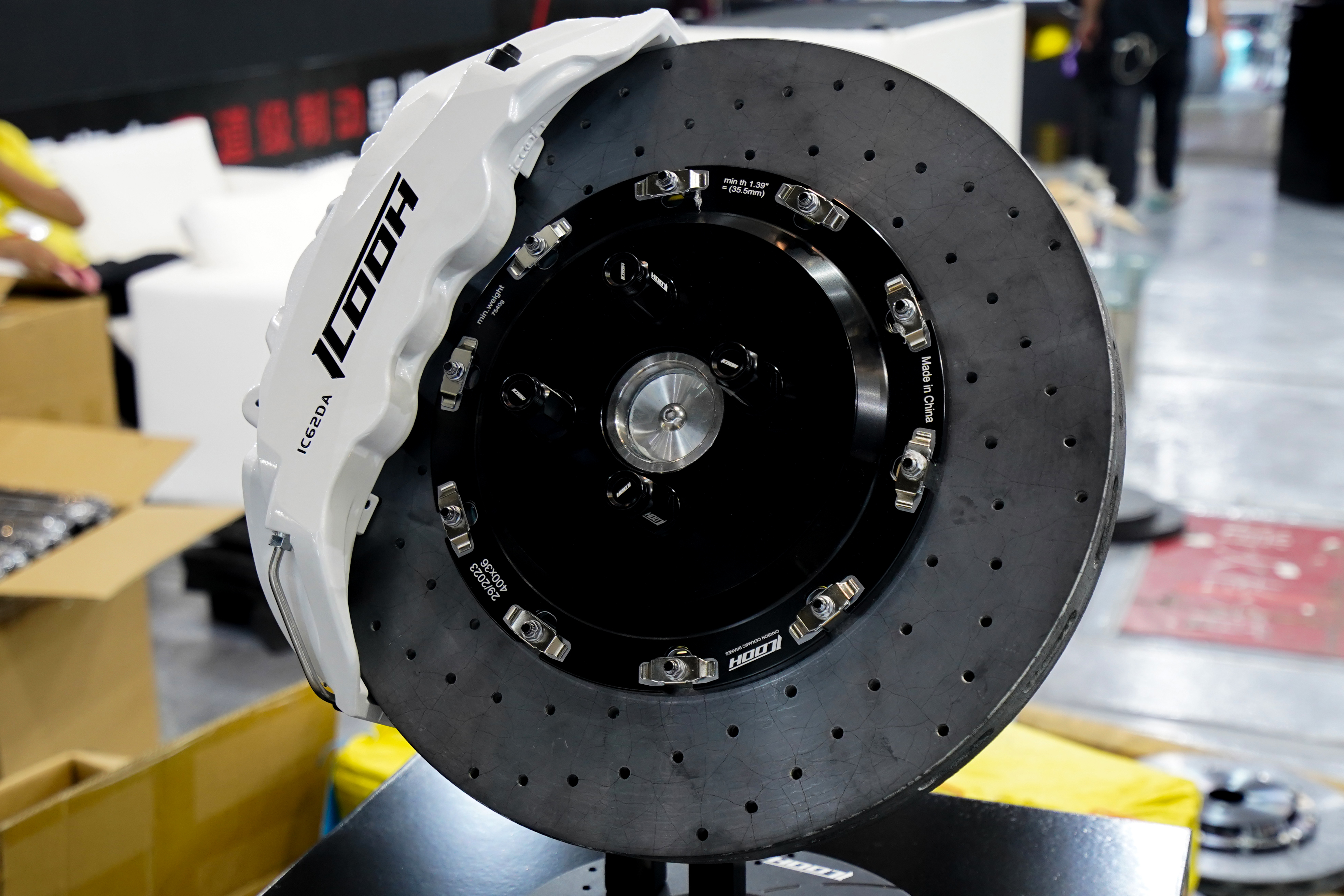
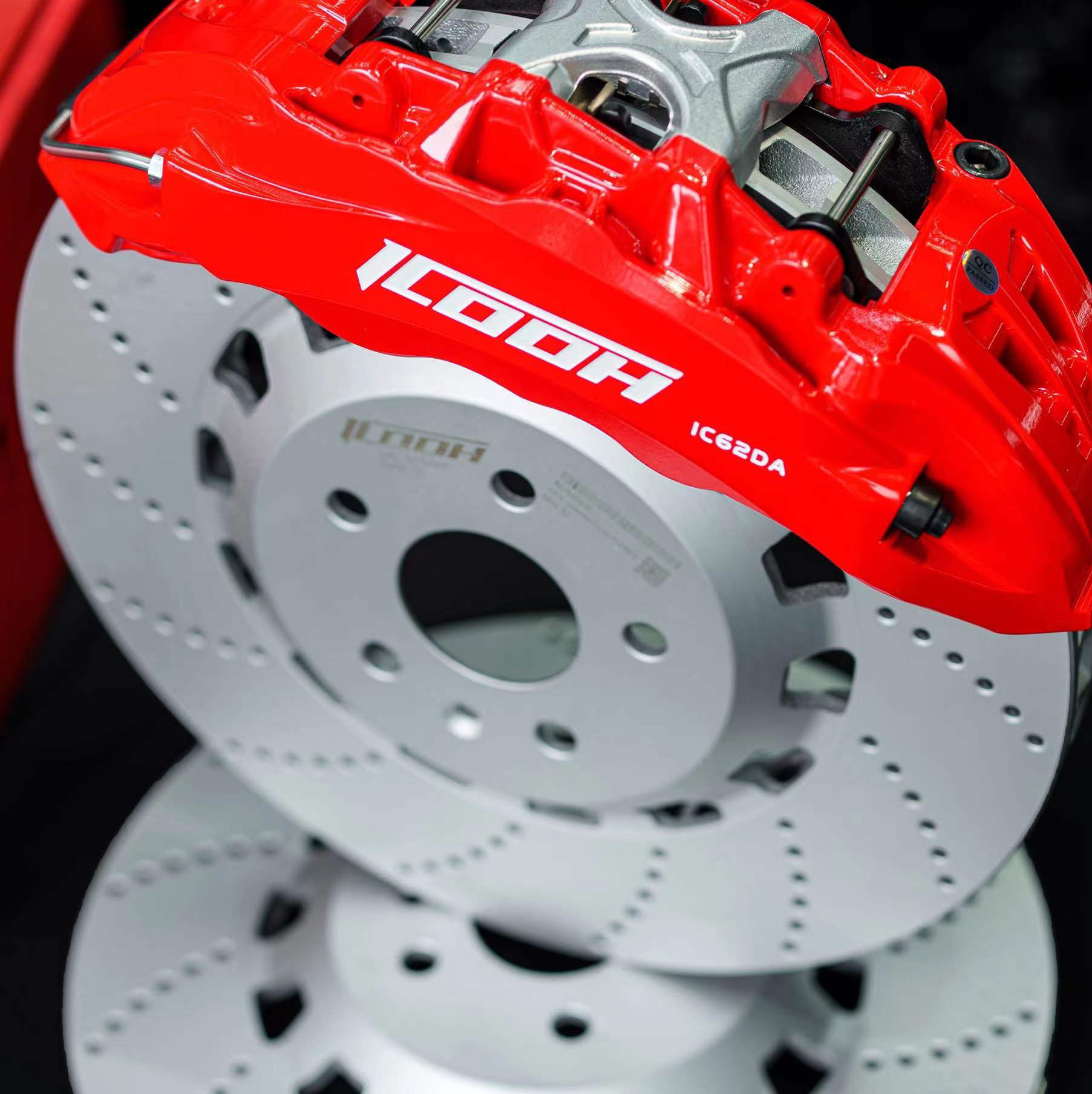
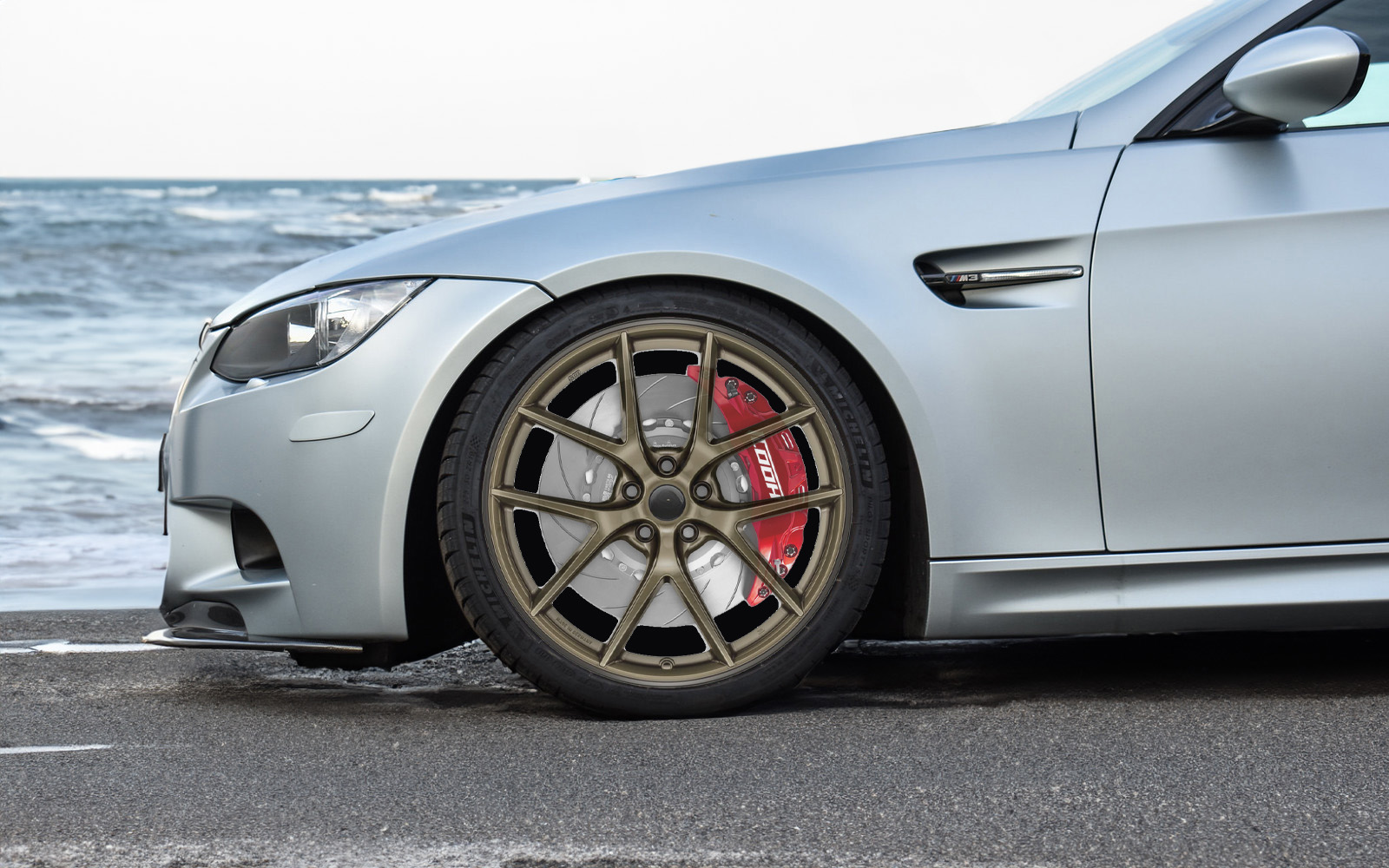
Different Types of Brake Discs Pros and Cons
Solid Discs:
- Pros:
- Simple and cost-effective design.
- Adequate braking performance for everyday driving.
- Cons:
- Prone to overheating under heavy or prolonged braking.
- Less effective heat dissipation compared to vented, cross-drilled, or slotted discs.
- Pros:
- Enhanced heat dispersion because of the inclusion of blades or fins between the brake surfaces.
- Reduced risk of brake fade, especially during heavy use or towing.
- Cons:
- Typically more expensive than solid discs.
- Heavier than solid discs because of the additional material.
Cross-Drilled Discs:
- Pros:
- Improved heat dissipation and gas release through the drilled holes.
- Enhanced braking performance, especially in high-performance or racing scenarios.
- Cons:
- Susceptible to cracking under extreme stress, particularly in racing conditions.
- Not as effective in wet conditions, as water can collect in the drilled holes and reduce friction.
Slotted Discs:
- Pros:
- Effective removal of gases and debris through the slots, maintaining consistent braking performance.
- Reduced risk of brake fade and improved brake bite.
- Cons:
- Can accelerate brake pad wear because of increased pad-to-disc contact.
- Slightly more prone to noise generation compared to other types of discs, especially when new.
- Pros:
- Lightweight design improves overall vehicle performance.
- Exceptional heat dissipation properties, providing consistent braking performance even under extreme conditions.
- Cons:
- Significantly more expensive than traditional cast iron discs.
- Limited availability and compatibility with certain vehicles due to their specialized nature.
It's important to consider factors such as driving habits, vehicle usage, budget, and performance requirements when selecting the appropriate type of brake discs for a vehicle.